



We get your business up and moving. We are a passionate bunch of number crunchers /budget heads. Whether it be an entire overhaul of your accounting department, managing your payrolling, or simply serving you as a bookkeeper – we are here.
Tax planning is a critical aspect of financial management for businesses and professionals. One of the key components of this process is Advance Tax, a system that mandates periodic tax payments throughout the financial year based on estimated income. This approach not only ensures compliance with tax regulations but also helps in better cash flow management and reduces the burden of last-minute tax liabilities.
Failure to make timely advance tax payments can result in interest penalties and financial strain, making it imperative for businesses and individuals to stay informed about due dates and best practices.
In this article, we’ll get deeper into the concept of Advance Tax Payments in India, outline the deadlines you need to focus on, and the best practices to ensure that payments are done on time.
Advance tax is a prepayment of income tax for income earned during a specific financial year. It applies to individuals who earn income beyond their regular salary, such as from capital gains, rental income, fixed deposits, and more.
Also termed as the “pay-as-you-earn” tax system, advance tax requires taxpayers to make payments during the year based on the expected income instead of a one-time lump payment at the end of the year.
This system is mandatory if the anticipated tax liability for the year exceeds ₹10,000, as per tax regulations. It helps ensure a continuous flow of revenue for the government while allowing taxpayers to manage their tax obligations more smoothly.
In India, the idea of advance tax has developed over the years. The Income Tax Act of 1961, which came into force on April 1, 1962, replaced the Indian Income Tax Act of 1922 and introduced comprehensive tax regulations, including provisions for advance tax payments. This system was designed to ensure a regular inflow of funds to the government and to distribute the tax burden more evenly across the year.
However, there is an exception: individuals over the age of 60 with no business revenue are not required to make advance tax payments.
In India, advance tax applies to individuals, professionals, and businesses whose estimated tax liability for the financial year exceeds ₹10,000. Below are the categories of taxpayers who are obligated to make advance tax payments:
Note: No interest under section 234C will be charged if you have paid up to 12% of the total advance tax in the first installment and up to 36% in the second installment.
For the Financial Year (FY) 2025-26, the advance tax payment schedule is as follows:
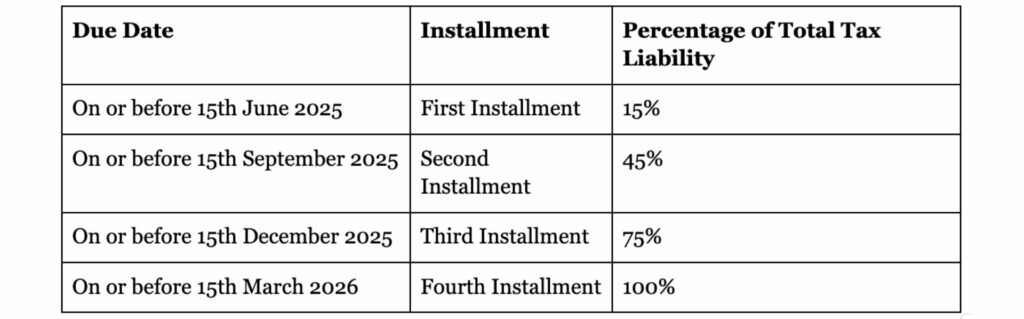
For taxpayers opting for the presumptive taxation scheme under Sections 44AD or 44ADA, the entire advance tax liability must be paid in a single installment by 15th March 2026. However, for this year, the deadline is 15th March 2025.
It’s important to note that the first installment is due on or before 15th June 2025, which is within the Financial Year 2025-26. Therefore, taxpayers should plan their finances accordingly to ensure timely payment and avoid any interest charges for late payments.
Advance tax payment calculations differ based on the tax regime you choose—Old Tax Regime or New Tax Regime. Each regime has distinct rules regarding deductions, exemptions, and tax slabs, which influence your advance tax liability.
Under the Old Tax Regime, taxpayers can avail of various deductions and exemptions, such as those under sections 80C and 80D, House Rent Allowance (HRA), and Leave Travel Allowance (LTA). To calculate advance tax under this regime:
On the other hand, the New tax regime offers reduced tax rates but eliminates most deductions and exemptions available under the Old Tax Regime. Since deductions and exemptions are not applicable, the New Tax Regime tax slabs can be directly applied to your total income. For the financial year 2025-26, the tax slabs are:
As per the Union Budget 2025, income up to ₹12 lakh is exempt from taxation under this regime. For employees, the limit is extended to ₹12.75 lakh.
Choosing between the Old and New Tax Regimes affects your advance tax obligations. If your estimated tax liability after TDS exceeds ₹10,000, you’re required to pay advance tax under both regimes. Failure to do so may result in interest charges of 1% per month on the overdue amount.
Also, while you can switch tax regimes when filing your Income Tax Return, it’s important to note that any changes in regime during the year can impact your advance tax calculations and potential interest liabilities.
It’s advisable to consult a chartered accountant to ensure accurate calculation and timely payment of advance tax, as they can provide personalized guidance based on your financial situation.
Late or insufficient advance tax payments in India can lead to significant financial consequences.
Under Section 234B of the Income Tax Act, if a taxpayer fails to pay at least 90% of their total tax liability by the end of the financial year, they are liable to pay interest at 1% per month on the unpaid amount from April 1st of the following financial year until the date of actual payment.
On top of that, Section 234C imposes interest at 1% per month on the shortfall in advance tax paid compared to the prescribed percentages by the due dates. For instance, if less than 75% of the tax liability is paid by December 15, interest is charged on the deficiency.
To mitigate these penalties, it’s advisable to maintain accurate financial records and seek professional bookkeeping services to ensure timely and accurate tax payments.
To manage these payments effectively and avoid penalties, consider the following best practices:
Regularly assessing your income is essential for accurate advance tax payments. By evaluating your earnings throughout the year, you can estimate your tax liability and make timely payments, thereby avoiding penalties.
For businesses, outsourcing accounting services to India can provide expert assistance in income assessment and tax planning, ensuring compliance and efficient financial management.
Adhering to advance tax payment deadlines is crucial to avoid interest penalties under Sections 234B and 234C of the Income Tax Act. To ensure timely payments, set reminders or utilize financial planning tools.
For comprehensive assistance, consider consulting professional taxation services. These experts can provide personalized guidance, helping you navigate complex tax regulations and optimize your tax planning strategies.
Engaging with experienced taxation services ensures compliance and effective management of your tax obligations.
Maintaining accurate records is key for effective auditing and accounting. Keeping track of all financial transactions and regularly checking accounts ensures your financial data stays correct.
This helps with filing taxes on time and makes audits smoother, as auditors need clear records to assess your finances. Efficient record-keeping improves transparency and builds trust with stakeholders, ensuring everything is in order when needed.
Planning for tax liabilities is essential for effective financial management. By setting aside funds regularly, you can ensure the timely payment of advance taxes and avoid penalties.
Using accounting and bookkeeping services can help maintain accurate financial records, identify potential tax-saving opportunities, and provide insights into your financial health. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also contributes to long-term financial stability.
Advance tax payments are essential for taxpayers in India to meet their tax obligations and avoid penalties. By adhering to the specified deadlines and following best practices, individuals and businesses can ensure compliance and maintain financial health.
If you are looking for experts to help your business with advance tax payments, GJM & Co is here to help. We offer services related to Financing, Taxation, bookkeeping and accounting services, Business Formation, payroll management, etc. You can get in touch with us via email at info@gjmco.com or can also schedule a call.