The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) has introduced a revised Guidance Note on the Preparation of Financial Statements of Non-Corporate Entities, published in August 2023, effective from April 1, 2025, covering financial periods starting April 1, 2024.
This comprehensive framework represents a transformational shift in financial reporting standards for businesses operating outside the corporate structure. The primary objective is to ensure standardization, promote transparency, and enhance comparability across non-corporate entities’ financial statements. In this article, we will cover this topic in detail.
Historical Context and Changes
The ICAI’s initiative to standardize financial reporting for non-corporate entities dates back several years, with preliminary technical guides issued in August 2023. The current guidance note evolved from these efforts, culminating in a comprehensive framework that aligns with modern accounting practices while recognizing the unique characteristics of non-corporate entities
The guidance note applies to a wide spectrum of non-corporate entities:
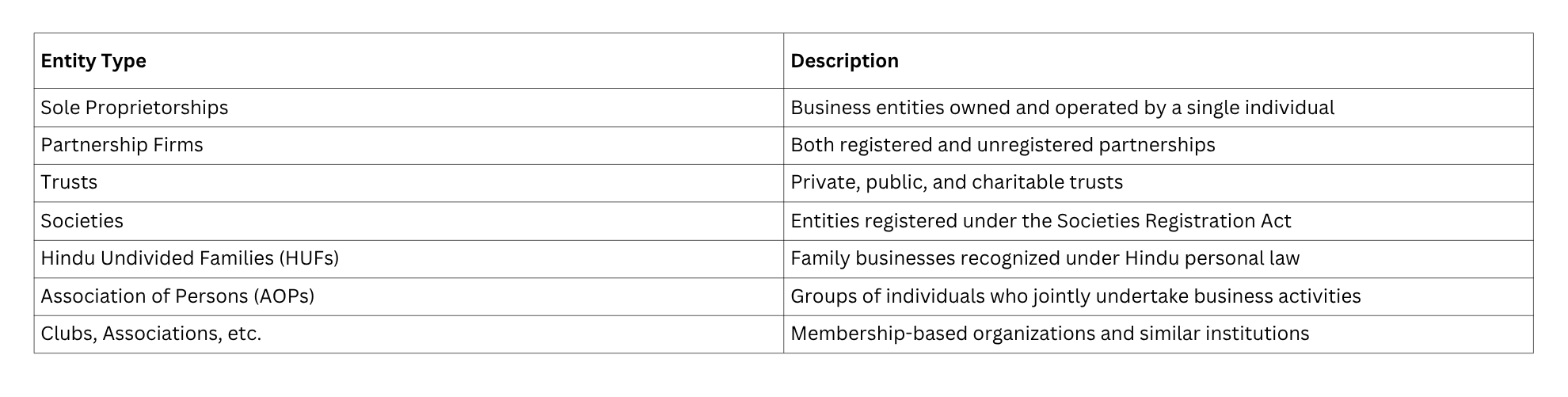
Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) are explicitly excluded from the purview of this guidance note as they are categorized as corporate entities subject to different reporting frameworks.
Entity Classification System
The guidance note introduces a four-tier classification system that determines compliance requirements based on size and financial exposure:
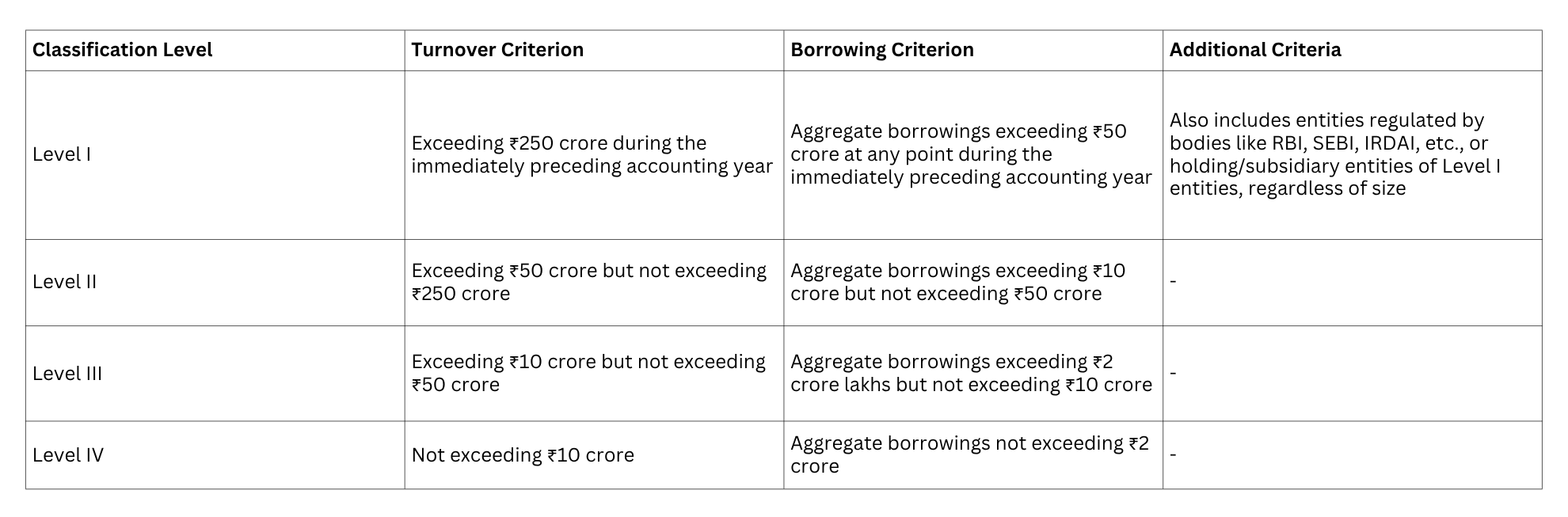
This classification is critical as it determines the extent of compliance required, with Level I entities subject to the most comprehensive reporting requirements and Level IV entities benefiting from maximum permissible exemptions.
Standardized Financial Statement Structure
The balance sheet provides information about an entity’s financial position. According to the Framework for the Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statements issued by ICAI, the elements directly related to the measurement of financial position are:
- An asset is a resource controlled by the enterprise as a result of past events from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise.
- A liability is a present obligation of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources embodying economic benefits.
- Equity is the residual interest in the assets of the enterprise after deducting all its liabilities.
The Guidance Note prescribes formats using the term ‘owners’ funds’ in place of ‘equity’ since some items of ‘owners’ funds’ may not strictly meet the definition of ‘equity’.
Here’s a table representation of the balance sheet structure:
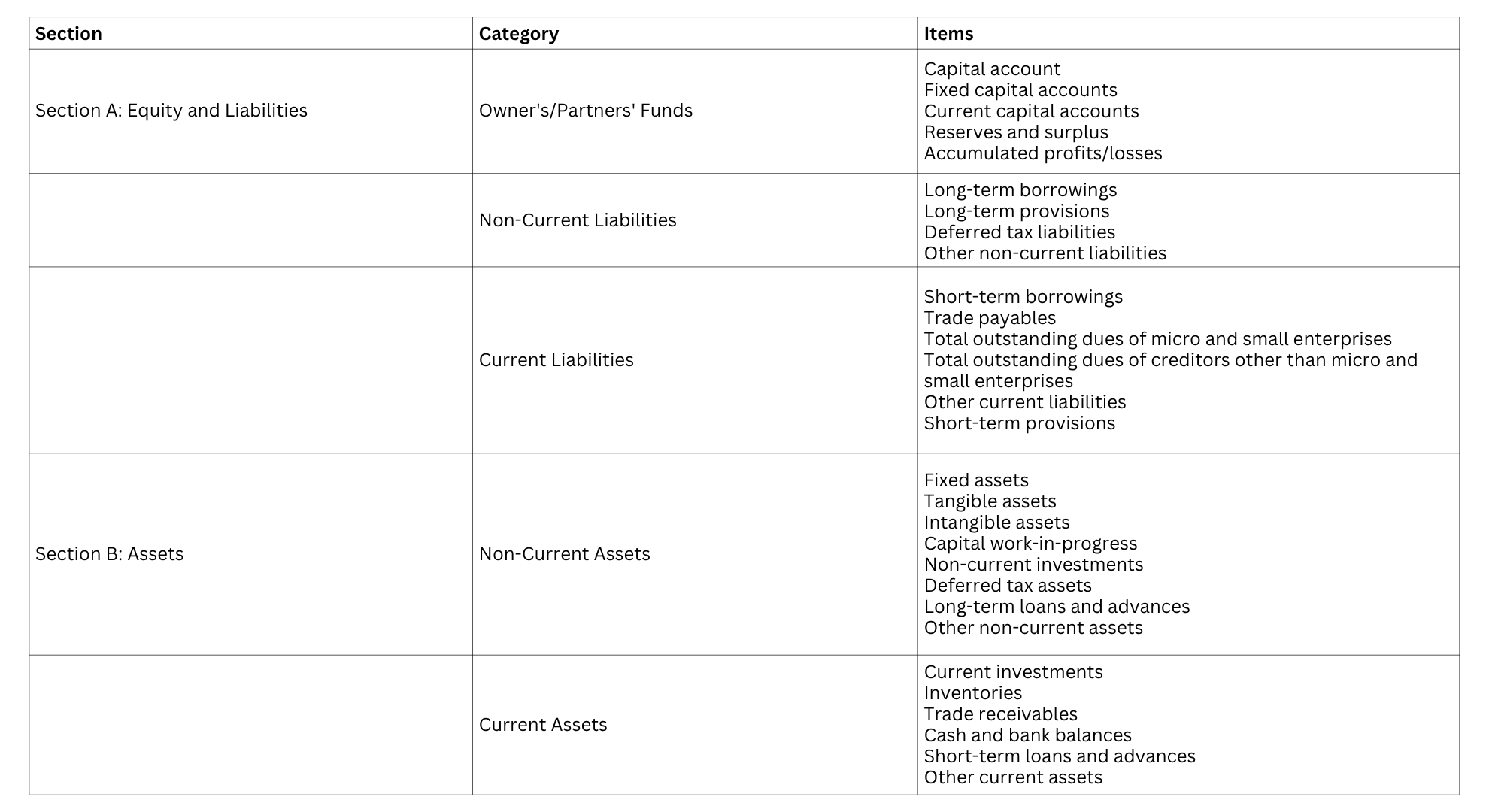
-
Statement of Profit and Loss
The Statement of Profit and Loss, also known as ‘Income Statement’ or ‘Profit & Loss Account’, reports an entity’s financial performance over a specific accounting period. It primarily focuses on income and expenses during a particular period.
- Income: Increase in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of inflows or enhancements of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to contributions from equity participants.
- Expenses: Decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or depletions of assets or incurrences of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to equity participants.
The statement of profit and loss follows a structured approach with:
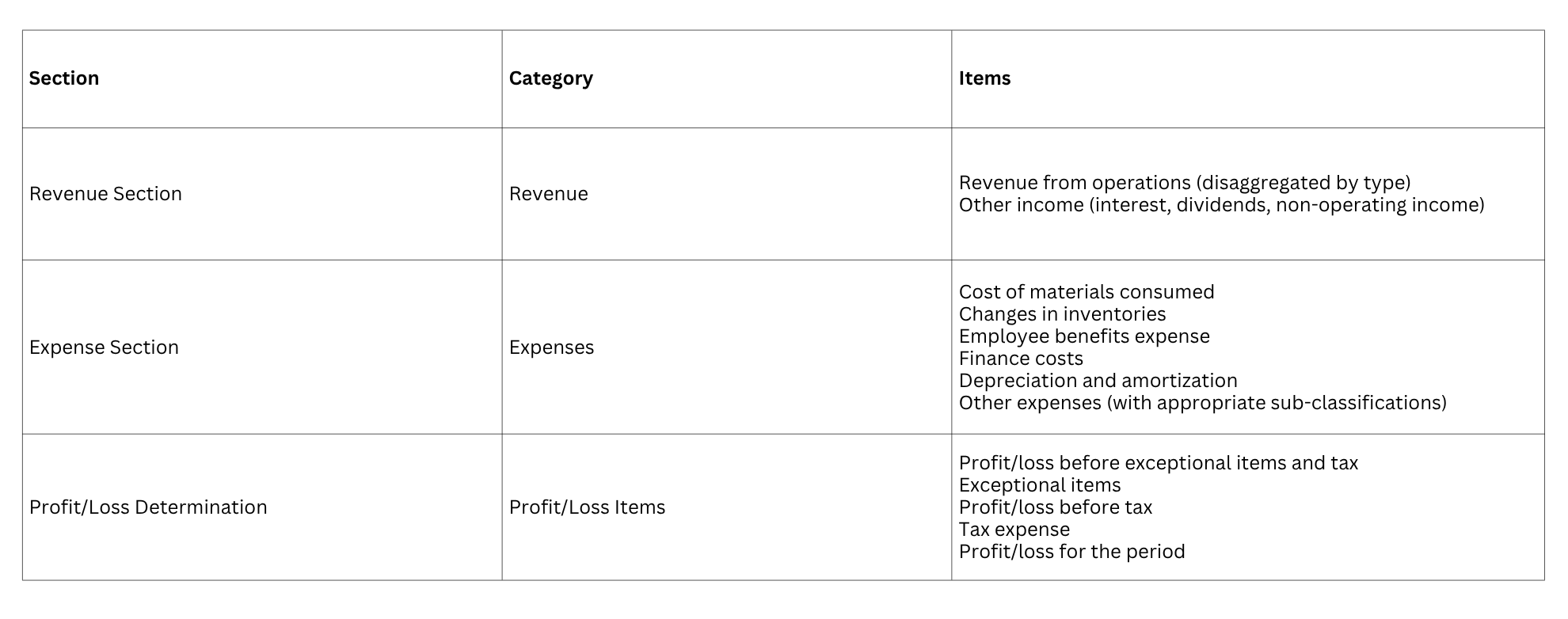
-
Cash Flow Statement Requirements
As per Accounting Standard (AS) 3, a cash flow statement, when used with other financial statements, enables users to evaluate changes in net assets, financial structure (including liquidity and solvency), and ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
Cash flow statements reconcile the income statement with the balance sheet through three major business activities:
- Operating Activities: Principal revenue-producing activities and other activities not classified as investing or financing. These include wages, income tax payments, interest payments, rent, and sales receipts.
- Investing Activities: Acquisitions and disposal of long-term assets and investments not included in cash equivalents. This category includes asset acquisitions/disposals and loans made to or repaid by third parties.
- Financing Activities: Activities changing the size and composition of owners’ capital and borrowings, including debt issuance, loans, and debt repayment.
For Micro, Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (Level IV, Level III and Level II non-company entities), cash flow statements are not mandatory but are encouraged.
The guidance note prescribes detailed requirements for cash flow statements:

For Level I and II entities, the cash flow statement must reconcile the opening and closing cash and cash equivalents, including bank overdrafts repayable on demand that form an integral part of the entity’s cash management system.
Format Requirements and Modifications
Financial statements must present a true and fair view of the entity’s state of affairs, comply with applicable Accounting Standards, and follow prescribed formats with these considerations:
- Formats may be modified to comply with relevant statutes and Accounting Standards applicable to non-corporate entities.
- Terminology may be amended based on entity type (e.g., “members’ funds” instead of “owners’ funds” for Associations of Persons).
- Disclosure requirements in the formats supplement rather than substitute those specified in Accounting Standards.
- Notes to accounts should provide additional information, narrative descriptions of statement items, and information about non-recognized items.
- Items on financial statements should cross-reference related information in the notes.
- Presentation should balance between excessive detail and important information.
- Figure rounding depends on the Total Income:
- Less than ₹100 crore: To nearest hundreds, thousands, lakhs, or millions
- ₹100 crore or more: To nearest lakhs, millions, or crores
- Once selected, measurement units should be used uniformly throughout the financial statements.
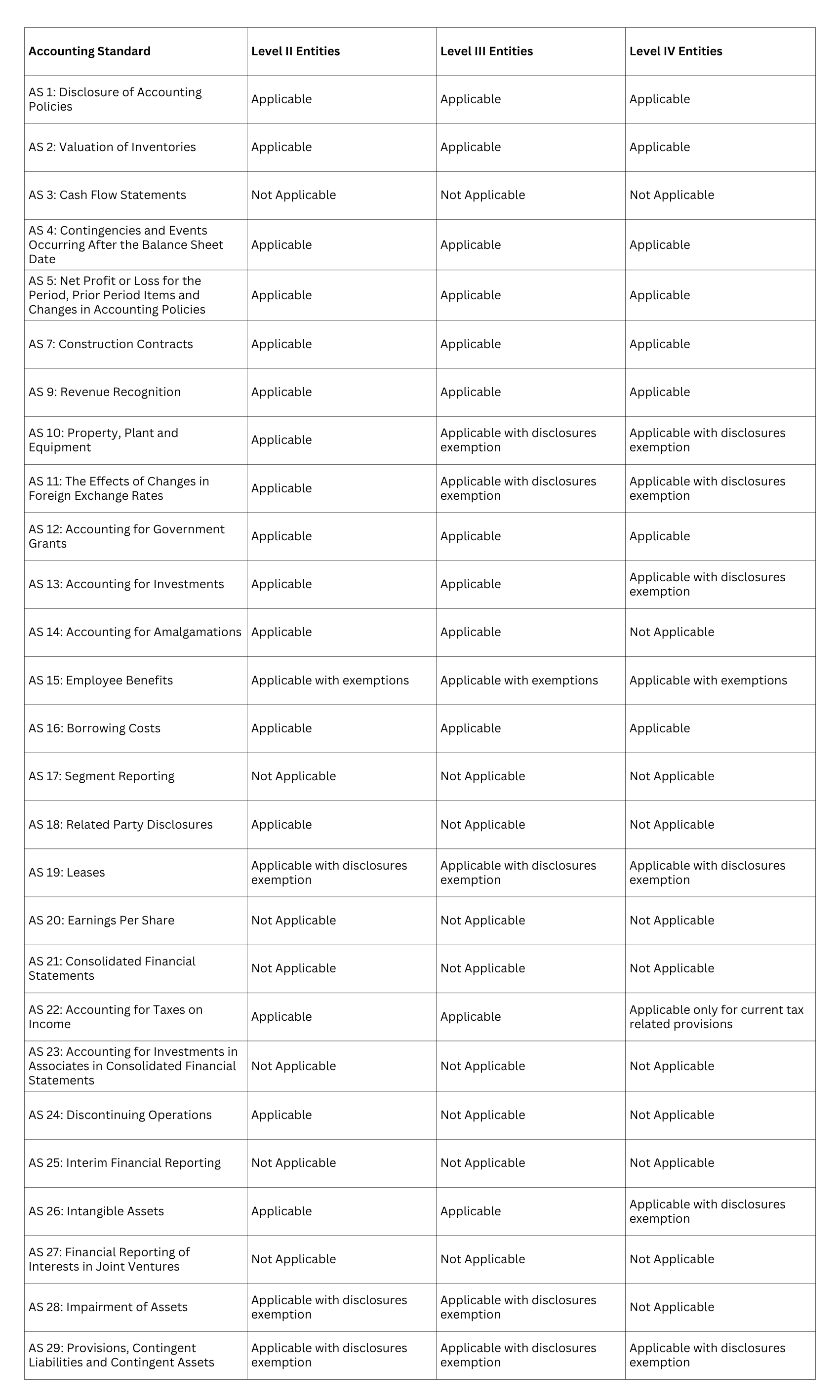
Applicability of Accounting Standards to Non-company Entities
The table below shows the applicability and exemptions for Level II, III, and IV Non-company entities:
Financial Instruments and Risk Management
The guidance note requires disclosures regarding:
- Classification and Measurement: Entities must disclose how they categorize their financial assets and liabilities, including fair value measurement methodologies and any reclassifications between categories during the reporting period.
- Risk Exposures: Financial statements must include information on the entity’s exposure to credit risk, liquidity risk, market risks (including interest rate, currency, and price vulnerabilities), and any significant concentration risks that could impact financial stability.
- Risk Management: Disclosures should explain the entity’s risk management objectives and policies, specific methods employed to measure various risk types, and any significant changes to risk management approaches from previous reporting periods.
What Are the Consequences of Non-Compliance?
Failure to adhere to the prescribed guidelines may result in:
- Regulatory Penalties: Entities may face fines or sanctions imposed by regulatory authorities for failing to follow the prescribed financial reporting guidelines.
- Audit Qualifications: Auditors may issue qualified opinions on financial statements that do not comply with the guidance note, significantly affecting the entity’s credibility.
- Stakeholder Trust Erosion: Non-compliance can lead to a loss of confidence from investors, creditors, and business partners who rely on accurate financial information.
- Legal Challenges: Entities may face potential litigation due to inadequate financial disclosure, particularly if stakeholders make decisions based on non-compliant financial statements.
- Financing Difficulties: Banks and lenders may hesitate to extend credit facilities to entities with non-compliant financial statements, viewing them as higher risk due to information quality concerns.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Based on early implementation experiences, entities should avoid:
- Using Old Formats: T-format balance sheets are prohibited under the new guidelines. Many entities also incorrectly mix elements of old and new formats, creating non-compliant hybrid statements.
- Missing Comparative Figures: Omitting prior year figures is explicitly non-compliant, as comparative information is mandatory. Inconsistent reclassification of prior year figures also leads to misleading comparisons.
- Boilerplate Accounting Policies: Generic policy templates fail to reflect entity-specific operations. Many entities also neglect to disclose significant judgments and estimates unique to their business.
- Tax-Focused Financials: Preparing statements primarily to align with tax requirements compromises accrual accounting principles. The failure to document and reconcile legitimate tax-GAAP differences creates compliance issues.
Conclusion
The ICAI’s revised guidance note marks a truly significant shift in financial reporting for India’s non-corporate entities. Business owners should take immediate steps to determine their classification level, carefully assess their current practices against the new requirements, and develop thoughtful implementation strategies.
To get assistance with the new guidelines, get in touch with GJM & Co. We offer services related to Taxation, Financing, Payroll Management, Bookkeeping and Accounting Services, Business Formation, and more. Email us at info@gjmco.com or call us to know more.









