



We get your business up and moving. We are a passionate bunch of number crunchers /budget heads. Whether it be an entire overhaul of your accounting department, managing your payrolling, or simply serving you as a bookkeeper – we are here.
The upcoming Direct Tax Code 2025 is a major step towards simplifying the country’s tax system. It aims to replace the old Income Tax Act of 1961 and the Wealth Tax Act of 1957 with clearer and more modern rules.
This new code is designed to make tax laws easier to understand, increase taxpayer base, reduce disputes, and align with global practices. It also brings changes to tax rates, residential status, and how certain incomes are taxed.
In this article, we will explore what the Direct Tax Code is, its key features, its impact on businesses, and more to help you understand this important reform.
The Direct Tax Code was introduced in the Budget to simplify, streamline, and standardize India’s complex income tax laws. Noticing the slow increase in the percentage of people contributing to income tax, the Indian government saw the need for a more straightforward version of tax rules and provisions. The main goal here is to make tax compliance easier for both individuals and businesses.
The Direct Tax Code 2025 introduces new tax slabs that are expected to benefit individuals earning up to ₹15 lakh annually. These changes might reduce the effective tax rates for middle-income earners, making the new tax regime more advantageous. The implication of this new Tax Code 2025 will take place from the coming financial year 2025-26.
Experts, including chartered accountants, believe that the simplified compliance processes and easier filing systems are significant improvements.
The Direct Tax Code (DTC) 2025 was introduced in Budget 2024-25 to overhaul India’s existing tax framework, aiming to create a more streamlined and efficient system. The primary objectives behind its introduction were:
For businesses, the DTC’s emphasis on simplification and transparency is expected to ease compliance processes.
Key changes affecting businesses include:
The Direct Tax Code (DTC) 2025 states a uniform corporate tax rate of 30% for both domestic and foreign companies. This change simplifies the tax structure, making it easier for businesses to understand their tax obligations.
Additionally, a standardized tax rate can enhance India’s attractiveness as a business destination, potentially leading to increased foreign investment and a more competitive business environment.
Under the Direct Tax Code 2025, capital gains taxation has been restructured. Short-term capital gains on financial assets will now likely incur a 20% tax rate, increased from 15%, while long-term gains will be taxed at 12.5%, reduced from 20%.
The higher tax on short-term gains may discourage quick asset turnovers, prompting companies to adopt longer investment horizons.
General Anti-Avoidance Rules (GAAR) empower tax authorities to invalidate business arrangements primarily designed for tax benefits without substantial commercial purpose.
This scrutiny challenges aggressive tax planning, compelling businesses to prioritize genuine economic activities over mere tax advantages.
Allowing Company Secretaries (CS) and Cost and Management Accountants (CMA) to conduct tax audits, previously exclusive to Chartered Accountants (CA), diversifies the tax auditing field.
This inclusion can streamline compliance processes, offering businesses more options for managing their financial audits.
The Direct Tax Code plans to eliminate numerous tax exemptions and deductions, but notably increasing the standard deduction for salaried employees by 50%, raising it from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000. This aims to simplify the tax system and broaden the tax base.
This change means individuals can no longer reduce their taxable income through various deductions, potentially leading to higher tax liabilities.
Let’s take a friendly look at how the new Direct Tax Code (DTC) 2025 compares to the old Income Tax Act (ITA) of 1961. Here’s a simple table to show you the main differences and what changes to expect:
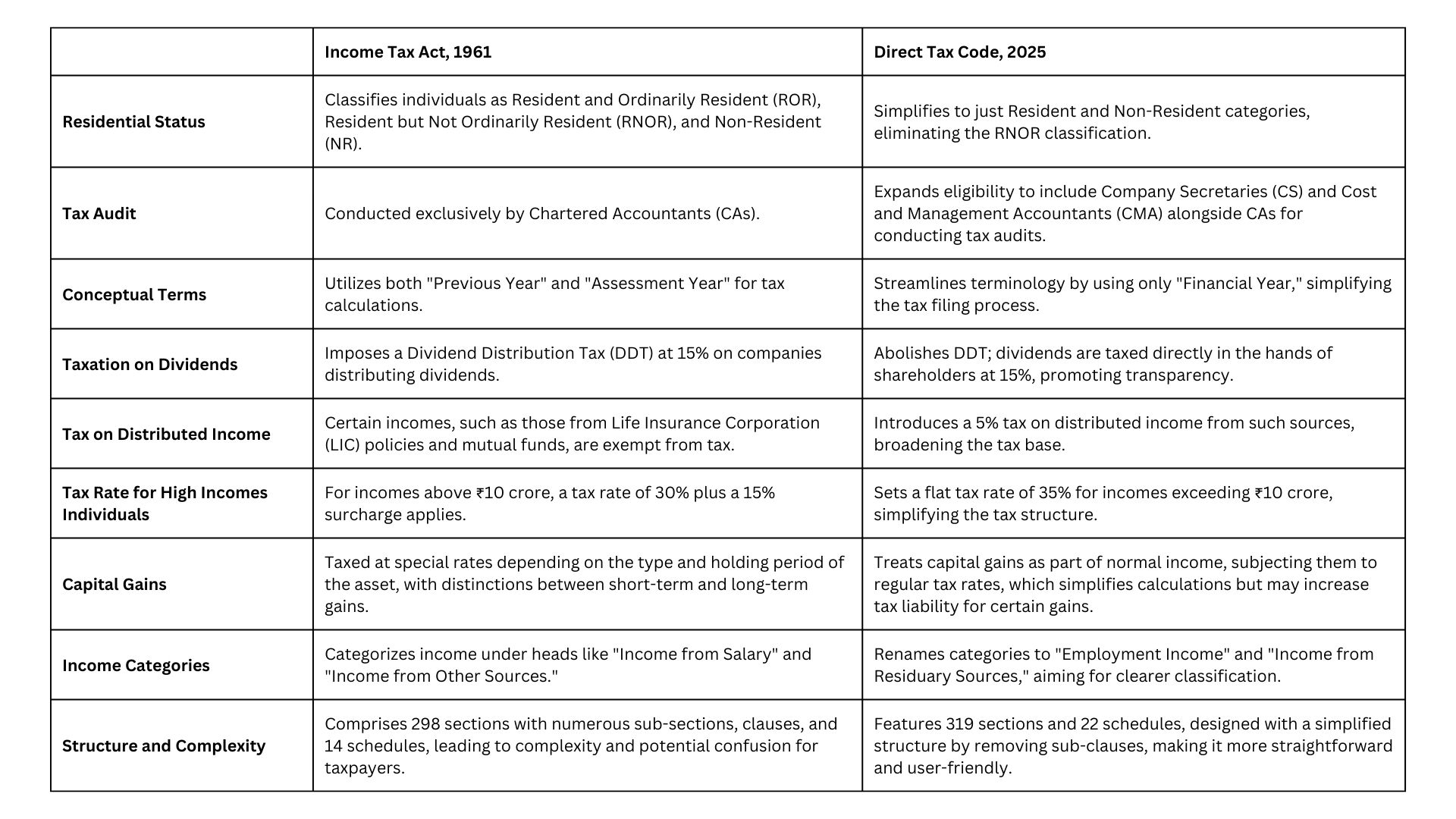
Conclusion
The Direct Tax Code (DTC) is set to replace the Income Tax Act of 1961, aiming to simplify India’s tax laws. This change will make the tax system fairer and easier for everyone to understand. While switching to the new system will require careful planning, the long-term benefits are expected to outweigh any initial challenges.
For Financing and Taxation services in India, consider GJM & Co. GJM & CO. offers a wide range of services including Business Formation, Payroll Management, Bookkeeping and Accounting Services, and more. Email us at info@gjmco.com or call us.